Table of Contents
Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder
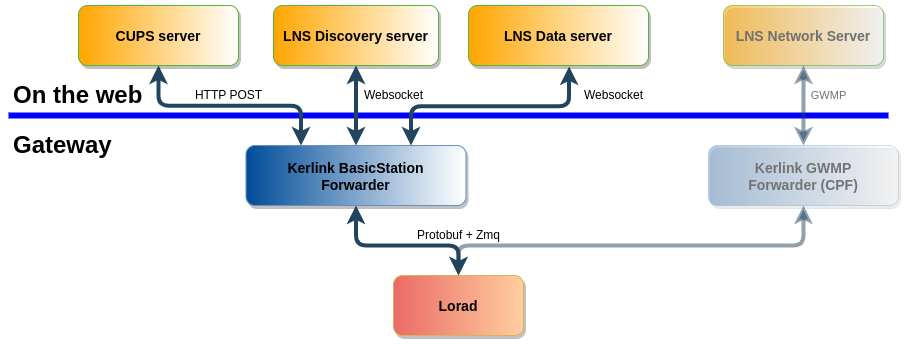
What is the Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder ?
Similarly to legacy (GWMP) packet forwarder, the Basic Station Packet Forwarder is a program running on a LoRa gateway. It forwards the LoRa packets emitted by end-devices and received by the gateway to a LoRa Network Server (LNS) and vice-versa, hence its name.
The Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder (BSPF) is based on “lorad” daemon from Common Packet Forwarder.
Once installed and configured, it is able to connect to a “LNS” or a “CUPS” server and handle all associated services (Radio configuration, Forward uplink packets, schedule downlink packets, etc.).
It implements the same protocols and authentication methods than Semtech LoRa Basics™ Station reference implementation.
What are the differences with Semtech LoRa Basics™ Station ?
The Semtech LoRa Basics™ Station is a nice reference implementation. But, as the original packet forwarder, it has the same drawbacks: It's a monolithic approach, designed to be hardly linked to the gateway radio architecture and to be used on one Network Server.
In other words, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder is the same package for all Kerlink iSeries gateways and can be configured while another previously-configured LNS is still functional.
Main features of reference implementation are implemented in Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder, including:
- CUPS and LNS protocols support
- TLS and Token-based Authentication
- Support for Class A and C on all gateways
- Support for main radio regions: EU868, US915, AS923, AU915 and IN865
The features not supported are listed below:
- timesync message: A ntpd daemon is embedded in all kerlink gateways and is much more precise than this time synchronization.
- Remote shell / remote command
The additional features:
- Packet buffering: Kerlink Basic Station Forwarder embeds a database to store uplink packets in case of LNS/Network disconnections.
- Multiple LNS connection: Kerlink Basic Station Forwarder can be used in same time than legacy (GWMP) forwarder allowing multiple LNS connections (see multiforwarder for further details)
Installation and configuration
If the software version of your gateway is not compatible, refer to resources section to upgrade to 5.x
Please see on AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN - Kerlink documentation for more information
Installation
- Download last version of Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder from the Basic Station resources page.
- Install the
basicstation_X.Y.Z_klkgw.ipkfile using the instructions of the software updates page.
The installation of the “basicstation” package adds the following content on the file system:
Kerlink CUPS configuration
After installation Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder is disabled by default. Once Basic Station Packet Forwarder started, if no configuration is available, it will connect to Kerlink CUPS using:
- cups-boot.uri
- cups-boot.key
- cups-boot.crt
Once connected to Kerlink CUPS, Basic Station Packet Forwarder will get its CUPS/LNS configuration.
It's now possible to set LNS configuration using Cockpit: Configure LoRaWAN with Wanesy Management Cockpit
Manual configuration
Once installed, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder is disabled by default. It should first be configured for the wanted server (CUPS and/or LNS).
As explained by Semtech documentation, the procedure to connect to server may differ depending on authentication mode used by server.
No authentication on LNS server
- URI of LNS server should be written in
/user/basic_station/etc/tc.uriconfig file. - Activate basicstation forwarder.
A tool named klk_bs_config is used to handle these steps.
TLS Server Authentication
Additionally to previous mode, a *.trust file should be provided to check server authenticity. (excepting for “Publicly known”/“Globally signed” certificates like “let's encrypt”, AWS, etc…)
TLS Server and Client Authentication
Additionally to previous mode, *.key and *.crt files should be provided to authenticate client (gateway) on server.
Example with an AWS CUPS server:
klk_bs_config --disable rm -f /user/basic_station/etc/*.key /user/basic_station/etc/*.trust /user/basic_station/etc/*.crt # Then, follow procedure depending on your LNS type
LNS Connection Status
Since version 2.5.0, the backhaul LEDs (Wirnet iFemtocell/iZeptocell) indicate the status of the LNS connection :
- a green LED indicates that connection to the LNS has been established
- a red LED indicates that connection has been either lost or not yet established
Advanced configuration
LBT/CCA specific case
For LNS which doesn't embed AS923-1 with LBT, it needs to be activated manually by using following commands:
# Disable current config klk_bs_config --disable # Use "Japan" lorad configuration explicitly and prevent from reconfiguration from LNS klk_bs_config --enable --loradconf AS923-1-JP.json --ignore-reconf
Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder configuration
By default, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder doesn't need any configuration files excepting those described above.
However, for advanced configuration, default settings can be modified by creating a configuration file named /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.
It allows to:
- Change log level (for whole application or component by component)
- Set router EUI
- Change CUPS request interval
- Activate packet buffering (database)
- Activate or disable websockets ping functionality (and set the ping interval)
An example of this configuration file is provided in /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.example.
Router EUI (for debug/test purpose)
Default Router EUI is the gateway EUI64 (printed on box and available in /tmp/board_info.json).
However, it can be overridden by setting it in this configuration file:
- Copy
/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.exampleto/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf - Edit
/user/basic_station/etc/station.confand locate[router]section - In this section, enter the line
id = <WANTED_EUI> - Save file
- Restart application
/etc/init.d/station restart
Packet buffering
Packet buffering allows to store uplink packets not transmitted to the LNS server when the link between gateway and server is broken.
The application will then retry periodically to re-connect to the LNS Server and as soon as the connection is back, all stored packets will be pushed in FIFO mode (First In, First Out) to respect packets chronology.
In order to activate it:
- Copy
/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.exampleto/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf - Edit
/user/basic_station/etc/station.confand locate the[database]section - Un-comment
enable = Trueline - Save file
- Restart application
/etc/init.d/station restart
Local DevAddr Filtering
In the case the LNS does not provide any NetID filter in the router_config message, it is possible to set local filters in order to only forward LoRa uplinks provided by a subset of devices.
To configure this feature, use the '-f' option of the klk_bs_config tool, and provide inclusive and/or exclusive filters to indicate the sets of DevAddr to be kept and/or rejected.
( see https://wikikerlink.fr/wirnet-productline/doku.php?id=wiki:lora:advanced_features#lorawan_frame_filtering for more details about filters values )
Local JoinEui Filtering
In the case the LNS does not provide any JoinEui filter in the router_config message, it is possible to set local filters in order to only forward LoRa JoinRequest matching by a subset of EUIs.
To configure this feature, use the '-j' option of the klk_bs_config tool, and provide inclusive and/or exclusive filters to indicate the sets of JoinEuis to be kept and/or rejected.
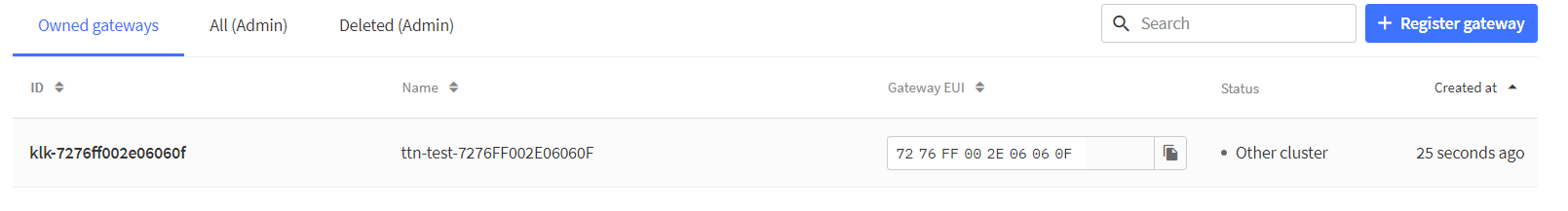
TTN LNS configuration tool
To ease declaration of a gateway on the TTN (thethings.network), TTI (thethings.industries) or TTS (The Things Stack Enterprise / Open Source) LNS, use the klk_ttn_config tool.
This tool adds the gateway on the server and creates its associated CUPS and LNS keys.
To use this tool, you need:
- an API token
- the API server URL
- the chose frequency plan
- On TTN
klk_ttn_configcan only be used one time per gateway due to certain TTN restrictions (even after removing the gateway from TTN)
- On TTI the gateway needs to be remove and purged in order to reuse
klk_ttn_config
klk_ttn_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
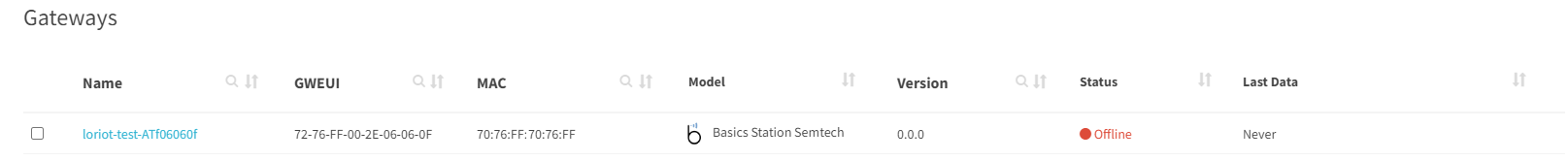
Loriot LNS configuration tool
To ease declaration of a gateway on the Loriot LNS, use the klk_loriot_config tool.
This tool creates the gateway on the server and installs the resulting LNS credentials on the gateway.
To use this tool, you need:
- an API key
- the API server URL
- a network ID
- LoRaWAN region
- region list:
- AU915-928
- AS923
- CN470-510
- CN779-787
- EU433
- EU863-870
- IN865-867
- KR920-923
- RU864-870
- US902-928
- Channel plans (1 to 8) comma separated (optional)
klk_loriot_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
AWS LNS configuration tool
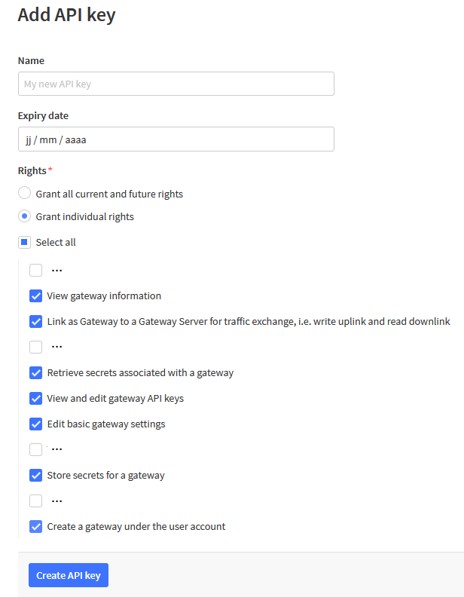
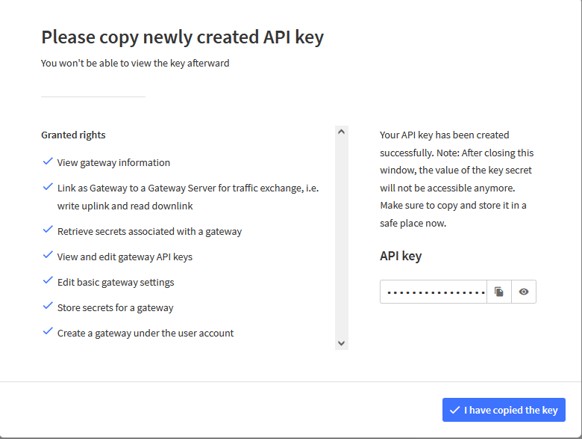
To ease declaration of a gateway on the AWS LNS, use the klk_aws_config tool.
This tool creates the gateway on the server and installs the resulting LNS credentials on the gateway.
To use this tool, you need:
- an API user ID
- an API key ID
- an API key secret
- the region of the AWS server the gateway will be declared on
- the LoRaWan region of the gateway
- the Frequency Sub Band(s) to use (required for US915 and AU915)
klk_aws_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
Actility LNS configuration tool
To ease declaration of a gateway on the Actility LNS, use the klk_actility_config tool.
This tool creates the gateway on the server and installs the resulting LNS credentials on the gateway.
To use this tool, you need:
- an API Client ID and its secret
- the API server URL
- the actility LoRaWAN region ID ( see https://oss-api.thingpark.com/tpe/7.3/Things-Management/network-manager/documentation-network-manager.html#/rf-regions )
klk_actility_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
Gateway name customization option
This option can be used to customize the gateway name displayed on LNS.
Optional parameters: --naming Set gateway naming strategy prefix[/scheme] schemes: "knet" : prefix-EUI[:-6] (default) "eui" : prefix-EUI "serial" : prefix-board serial "model" : model-EUI[:-6]