Setups
General information
Wirnet™ iBTS information
Wirnet™ iFemtoCell information
Wirnet™ iFemtoCell-evolution information
Wirnet™ iStation information
System management
Network management
LoRa Features
KerOS customization
Support and resources
Setups
General information
Wirnet™ iBTS information
Wirnet™ iFemtoCell information
Wirnet™ iFemtoCell-evolution information
Wirnet™ iStation information
System management
Network management
LoRa Features
KerOS customization
Support and resources
This is an old revision of the document!
Similarly to legacy (GWMP) packet forwarder, the Basic Station Packet Forwarder is a program running on a LoRa gateway. It forwards the LoRa packets emitted by end-devices and received by the gateway to a LoRa Network Server (LNS) and vice-versa, hence its name.
The Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder (BSPF) is based on “lorad” daemon from Common Packet Forwarder.
Once installed and configured, it is able to connect to a “LNS” or a “CUPS” server and handle all associated services (Radio configuration, Forward uplink packets, schedule downlink packets, etc.).
It implements the same protocols and authentication methods than Semtech LoRa Basics™ Station reference implementation.
The Semtech LoRa Basics™ Station is a nice reference implementation. But, as the original packet forwarder, it has the same drawbacks: It's a monolithic approach, designed to be hardly linked to the gateway radio architecture and to be used on one Network Server.
In other words, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder is the same package for all Kerlink iSeries gateways and can be configured while another previously-configured LNS is still functional.
Main features of reference implementation are implemented in Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder, including:
The features not supported are listed below:
The additional features:
If the software version of your gateway is not compatible, refer to resources section to upgrade to 5.x
basicstation_X.Y.Z_klkgw.ipk file using the instructions of the software updates page.The installation of the “basicstation” package adds the following content on the file system:
/ ├── etc │ ├── default │ │ └── station │ ├── init.d │ │ └── station │ ├── logrotate.d │ │ └── station │ ├── monit.d │ │ └── station │ ├── profile.d │ │ └── station │ ├── rcK.d │ │ └── K52station -> ../init.d/station │ ├── rcU.d │ │ └── S51station -> ../init.d/station │ ├── rsyslog.d │ │ └── station │ └── sysupgrade.d │ └── basic_station.conf └── user └── basic_station ├── bin │ ├── klk_bs_config │ ├── klk_loriot_config │ ├── klk_ttn_config │ └── station ├── etc │ └── station.conf.example └── lib └── python3.10 └── site-packages ├── basicstation │ └── [...] └── basicstation-X.Y.Z-py3.10.egg-info └── [...]
Once installed, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder is disabled by default. It should first be configured for the wanted server (CUPS and/or LNS).
As explained by Semtech documentation, the procedure to connect to server may differ depending on authentication mode used by server.
/user/basic_station/etc/tc.uri config file.
A tool named klk_bs_config is used to handle these steps.
With a Chirpstack-based LNS server named lns.local
klk_bs_config --enable --lns-uri "ws://lns.local:3001"
Additionally to previous mode, a *.trust file should be provided to check server authenticity. (excepting for “Publicly known”/“Globally signed” certificates like “let's encrypt”, AWS, etc…)
1 - With a Chirpstack-based LNS server named lns.local with a reference certificate named ca_cert
cp ca_cert /user/basic_station/etc/tc.trust klk_bs_config --enable --lns-uri "wss://lns.local:3001"
2 - With a CUPS server named cups.local with a reference certificate named ca_cert:
cp ca_cert /user/basic_station/etc/cups.trust klk_bs_config --enable --cups-uri "https://cups.local"
Additionally to previous mode, *.key and *.crt files should be provided to authenticate client (gateway) on server.
Example with an AWS CUPS server:
xxx.cert.pem: the (public) certificate of the gateway.xxx.private.key: private key of gateway.
Additionally, the CUPS endpoint should be known. In this example https://XXX.cups.lorawan.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com will be used. The certificate of this server is globally signed so .trust file is not needed.
xxx.private.key and certificate xxx.cert.pem on gatewaycp xxx.private.key /user/basic_station/etc/cups.key cp xxx.cert.pem /user/basic_station/etc/cups.crt
klk_bs_config --enable --cups-uri "https://XXX.cups.lorawan.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com"
klk_bs_config --disable rm -f /user/basic_station/etc/*.key /user/basic_station/etc/*.trust /user/basic_station/etc/*.crt # Then, follow procedure depending on your LNS type
Since version 2.5.0, the backhaul LEDs (Wirnet iFemtocell/iZeptocell) indicate the status of the LNS connection :
By default, LBT is NOT activated for AS923-1 region. It needs to be activated manually by using following commands:
# Disable current config klk_bs_config --disable # Use "Japan" lorad configuration explicitly and prevent from reconfiguration from LNS klk_bs_config --enable --loradconf AS923-1-JP.json --ignore-reconf
By default, Kerlink Basic Station Packet Forwarder doesn't need any configuration files excepting those described above.
However, for advanced configuration, default settings can be modified by creating a configuration file named /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.
It allows to:
An example of this configuration file is provided in /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.example.
Default Router EUI is the gateway EUI64 (printed on box and available in /tmp/board_info.json).
However, it can be overridden by setting it in this configuration file:
/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.example to /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf and locate [router] sectionid = <WANTED_EUI>/etc/init.d/station restartPacket buffering allows to store all uplink packets not correctly transmitted to LNS server.
Application will then retry periodically to re-connect to LNS Server and as soon as the connection is back, all stored packets will be pushed in FIFO mode (First In, First Out) to respect packets chronology.
In order to activate it:
/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf.example to /user/basic_station/etc/station.conf/user/basic_station/etc/station.conf and locate [database] sectionenable = True line/etc/init.d/station restart
To ease declaration of a gateway on the TTN (thethings.network), TTI (thethings.industries) or TTS (The Things Stack Enterprise / Open Source) LNS, use the klk_ttn_config tool.
This tool adds the gateway on the server and creates its associated CUPS and LNS keys.
To use this tool, you need:
klk_bs_config is still required after this to complete the Basic Station configuration.
klk_ttn_config can only be used one time per gateway due to certain TTN restrictions (even after removing the gateway from TTN)klk_ttn_config
# Use TTN configuration tool for TTN LNS klk_ttn_config -u https://eu1.cloud.thethings.network -t NNSXS.R6D3ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI.ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ -f EU_863_870 # Use TTN configuration tool for TTI LNS where tenant is your Tenant ID klk_ttn_config -u https://tenant.eu1.cloud.thethings.industries -t NNSXS.R6D3ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI.ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ -f EU_863_870
klk_ttn_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
How to generate an TTI API key?
Prerequisite: You have to create a TTI account
To automatically connect Kerlink Gateways to TTI LNS, you have to delegate some rights to Kerlink thanks to an “API key”. Please follow those steps:
Step 1 - Connect to your TTI user account
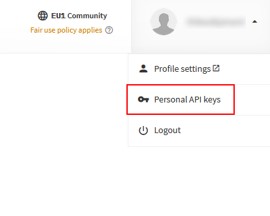
Step 2 - Go to Personal API keys OR TTI organization API key
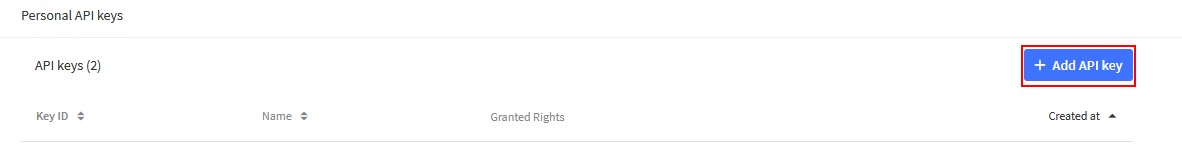
Step 3 - Add a new API key
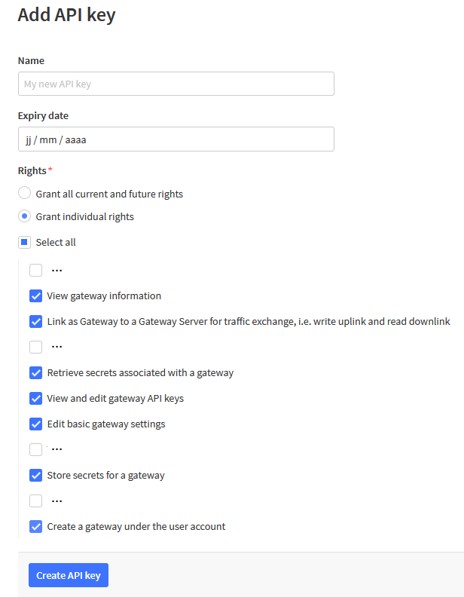
Step 4 - Create the API key with rights limited to GW creation and edition
Step 5 - Save API key
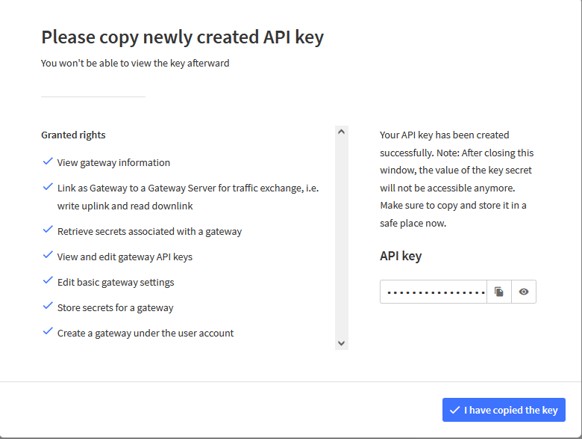
To ease declaration of a gateway on the Loriot LNS, use the klk_loriot_config tool.
This tool creates the gateway on the server and installs the resulting LNS credentials on the gateway.
To use this tool, you need:
klk_bs_config is still required after this to complete the Basic Station configuration.
# Use Loriot configuration tool in region US902 with 3 channel plans (US915_CH16_23, US915_CH40_47 and US915_CH56_63) klk_loriot_config -k ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJK-321abcdefgh -u https://eu1.loriot.io/1/nwk -n ABCD1234 -r US902-928 -p 3,6,8 # Disable websocket pings klk_bs_config --enable --ping_interval None
klk_loriot_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
To ease declaration of a gateway on the AWS LNS, use the klk_aws_config tool.
This tool creates the gateway on the server and installs the resulting LNS credentials on the gateway.
To use this tool, you need:
klk_bs_config is still required after this to complete the Basic Station configuration.
# Use AWS configuration tool klk_aws_config -u some_user -k ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST-s ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMN-r eu-west-1 -l US915 -f 1 -b
klk_aws_config tool has been designed to be called from a Zero Touch Provisioning job.
This option can be used to customize the gateway name displayed on LNS.
Optional parameters: --naming Set gateway naming strategy prefix[/scheme] schemes: "knet" : prefix-EUI[:-6] (default) "eui" : prefix-EUI "serial" : prefix-board serial "model" : model-EUI[:-6]
# Use TTN configuration tool klk_ttn_config -u https://eu1.cloud.thethings.network -t NNSXS.R6D3ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI.ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ -f EU_863_870 --naming ttn-test/eui
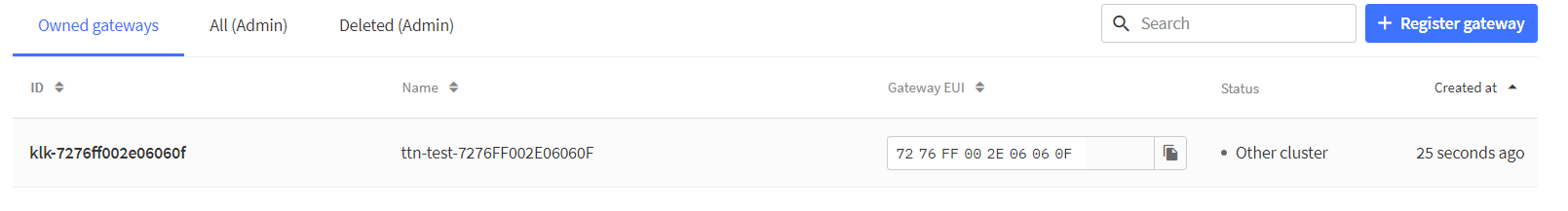
# Use Loriot configuration tool klk_loriot_config -k ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJK-321abcdefgh -u https://eu1.loriot.io/1/nwk -n ABCD1234 -r US902-928 -p 3,6,8 --naming loriot-test/serial
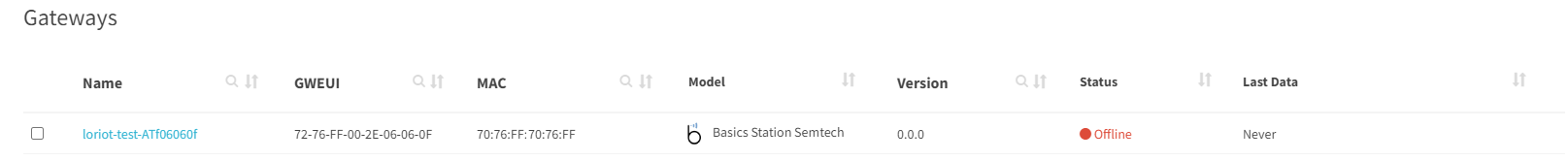
# Use AWS configuration tool klk_aws_config -u some_user -k ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST-s ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMN-r eu-west-1 -l US915 -f 1 -b --naming aws-test/knet
